on video MULTIVIBRADOR ASTÁVEL COM NPN E PNP
MULTIVIBRADOR ASTÁVEL COM NPN E PNP
Astable Multivibrators are free running oscillators which oscillate between two states continually producing two square wave output waveforms
Regenerative switching circuits such as Astable Multivibrators are the most commonly used type of relaxation oscillator because not only are they simple, reliable and ease of construction they also produce a constant square wave output waveform.
Unlike the Monostable Multivibrator or the Bistable Multivibrator we looked at in the previous tutorials that require an “external” trigger pulse for their operation, the Astable Multivibrator has automatic built in triggering which switches it continuously between its two unstable states both set and reset.
The Astable Multivibrator is another type of cross-coupled transistor switching circuit that has NO stable output states as it changes from one state to the other all the time. The stable circuit consists of two switching transistors, a cross-coupled feedback network, and two time delay capacitors which allows oscillation between the two states with no external triggering to produce the change in state.
In electronic circuits, stable multivibrators are also known as Free-running Multivibrator as they do not require any additional inputs or external assistance to oscillate. Stable oscillators produce a continuous square wave from its output or outputs, (two outputs no inputs) which can then be used to flash lights or produce a sound in a loudspeaker.
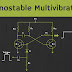
The basic transistor circuit for an Astable Multivibrator produces a square wave output from a pair of grounded emitter cross-coupled transistors. Both transistors either NPN or PNP, in the multivibrator are biased for linear operation and are operated as Common Emitter Amplifiers with 100% positive feedback.
This configuration satisfies the condition for oscillation when: ( βA = 1∠ 0o ). This results in one stage conducting “fully-ON” (Saturation) while the other is switched “fully-OFF” (cut-off) giving a very high level of mutual amplification between the two transistors. Conduction is transferred from one stage to the other by the discharging action of a capacitor through a resistor as shown below.
MULTIVIBRADOR ASTÁVEL COM NPN E PNP
Astable Multivibrators are free running oscillators which oscillate between two states continually producing two square wave output waveforms
Regenerative switching circuits such as Astable Multivibrators are the most commonly used type of relaxation oscillator because not only are they simple, reliable and ease of construction they also produce a constant square wave output waveform.
Unlike the Monostable Multivibrator or the Bistable Multivibrator we looked at in the previous tutorials that require an “external” trigger pulse for their operation, the Astable Multivibrator has automatic built in triggering which switches it continuously between its two unstable states both set and reset.
The Astable Multivibrator is another type of cross-coupled transistor switching circuit that has NO stable output states as it changes from one state to the other all the time. The stable circuit consists of two switching transistors, a cross-coupled feedback network, and two time delay capacitors which allows oscillation between the two states with no external triggering to produce the change in state.
In electronic circuits, stable multivibrators are also known as Free-running Multivibrator as they do not require any additional inputs or external assistance to oscillate. Stable oscillators produce a continuous square wave from its output or outputs, (two outputs no inputs) which can then be used to flash lights or produce a sound in a loudspeaker.
The basic transistor circuit for an Astable Multivibrator produces a square wave output from a pair of grounded emitter cross-coupled transistors. Both transistors either NPN or PNP, in the multivibrator are biased for linear operation and are operated as Common Emitter Amplifiers with 100% positive feedback.
This configuration satisfies the condition for oscillation when: ( βA = 1∠ 0o ). This results in one stage conducting “fully-ON” (Saturation) while the other is switched “fully-OFF” (cut-off) giving a very high level of mutual amplification between the two transistors. Conduction is transferred from one stage to the other by the discharging action of a capacitor through a resistor as shown below.







No comments