on video The Making of a loudspeaker voice coil
Voice Coil Fundamentals
This chapter will discuss the design features and functions of voice coils.
What are Voice Coils?
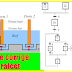
A voice coil is a winding of a wire, usually copper, aluminum, or copper-clad aluminum that is wrapped around a former (often called a bobbin) and then attached to the apex of a speaker cone. This voice coil results in the movement of the speaker cone by reacting to the magnetic field of the motor structure.
A magnetic field is created when a current is sent through a speaker or subwoofer's voice coil. This magnetic field is created within the gap between the magnet structure and the voice coil. This reaction results in the movement of the coil. As in music, a waveform is added, and the cone will react by reproducing the music or audio signal.
In the voice coil actuator working principle, the current that carries the inductors’ interactions within a permanent magnetic field generates a force. This force is proportional to the product of the magnetic flux and current in the coil. The Lorenz equation of force depicts this:
F=B×I
Where F is the Force (N), B is the magnetic Flux density (Tesla), and I is the Current (Amps).
Throughout the stroke of the actuator, the generated force is typically constant, although it can minutely decrease at the start and end of the stroke.
The moving element of the actuator can either be the assembly of the coil or of the permanent magnetic field.
Voice Coil Fundamentals
This chapter will discuss the design features and functions of voice coils.
What are Voice Coils?
A voice coil is a winding of a wire, usually copper, aluminum, or copper-clad aluminum that is wrapped around a former (often called a bobbin) and then attached to the apex of a speaker cone. This voice coil results in the movement of the speaker cone by reacting to the magnetic field of the motor structure.
A magnetic field is created when a current is sent through a speaker or subwoofer's voice coil. This magnetic field is created within the gap between the magnet structure and the voice coil. This reaction results in the movement of the coil. As in music, a waveform is added, and the cone will react by reproducing the music or audio signal.
In the voice coil actuator working principle, the current that carries the inductors’ interactions within a permanent magnetic field generates a force. This force is proportional to the product of the magnetic flux and current in the coil. The Lorenz equation of force depicts this:
F=B×I
Where F is the Force (N), B is the magnetic Flux density (Tesla), and I is the Current (Amps).
Throughout the stroke of the actuator, the generated force is typically constant, although it can minutely decrease at the start and end of the stroke.
The moving element of the actuator can either be the assembly of the coil or of the permanent magnetic field.
Voice Coil Fundamentals
This chapter will discuss the design features and functions of voice coils.
What are Voice Coils?
A voice coil is a winding of a wire, usually copper, aluminum, or copper-clad aluminum that is wrapped around a former (often called a bobbin) and then attached to the apex of a speaker cone. This voice coil results in the movement of the speaker cone by reacting to the magnetic field of the motor structure.
A magnetic field is created when a current is sent through a speaker or subwoofer's voice coil. This magnetic field is created within the gap between the magnet structure and the voice coil. This reaction results in the movement of the coil. As in music, a waveform is added, and the cone will react by reproducing the music or audio signal.
In the voice coil actuator working principle, the current that carries the inductors’ interactions within a permanent magnetic field generates a force. This force is proportional to the product of the magnetic flux and current in the coil. The Lorenz equation of force depicts this:
F=B×I
Where F is the Force (N), B is the magnetic Flux density (Tesla), and I is the Current (Amps).
Throughout the stroke of the actuator, the generated force is typically constant, although it can minutely decrease at the start and end of the stroke.
The moving element of the actuator can either be the assembly of the coil or of the permanent magnetic field.
Voice Coil Fundamentals
This chapter will discuss the design features and functions of voice coils.
What are Voice Coils?
A voice coil is a winding of a wire, usually copper, aluminum, or copper-clad aluminum that is wrapped around a former (often called a bobbin) and then attached to the apex of a speaker cone. This voice coil results in the movement of the speaker cone by reacting to the magnetic field of the motor structure.
A magnetic field is created when a current is sent through a speaker or subwoofer's voice coil. This magnetic field is created within the gap between the magnet structure and the voice coil. This reaction results in the movement of the coil. As in music, a waveform is added, and the cone will react by reproducing the music or audio signal.
In the voice coil actuator working principle, the current that carries the inductors’ interactions within a permanent magnetic field generates a force. This force is proportional to the product of the magnetic flux and current in the coil. The Lorenz equation of force depicts this:
F=B×I
Where F is the Force (N), B is the magnetic Flux density (Tesla), and I is the Current (Amps).
Throughout the stroke of the actuator, the generated force is typically constant, although it can minutely decrease at the start and end of the stroke.
The moving element of the actuator can either be the assembly of the coil or of the permanent magnetic field.







No comments