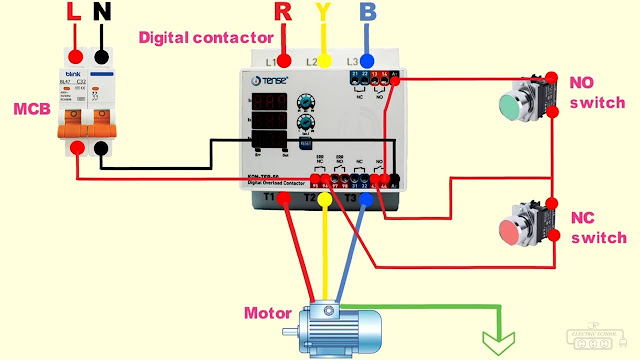
ON VIDEO Digital contactor 3 phase dol starter connection
Different starting methods are used for starting induction motors because the induction motor draws more starting current when starting. In order to avoid damage to windings due to high starting current flow, we use different types of starters.
The simplest form of motor starter for the induction motor is the Direct On Line Starter. The direct-on-line (DOL) starter includes a circuit breaker, contactor and overload relay for protection. Electromagnetic contactor which can be opened by the thermal relay in the event of a fault.
Typically the contactor will be controlled by separate start and stop buttons and an auxiliary contact on the contactor is used, opposite the start button, as a hold contact. That is to say. the contactor is electrically interlocked and closed during engine operation.
Principle of the direct on-line starter (DOL)
To begin with, the contactor is closed, applying line voltage to the motor windings. The motor will draw a very high inrush current for a very short time, the magnetic field in the iron, and then the current will be limited to the locked rotor current of the motor. The motor will develop locked rotor torque and begin to accelerate to maximum speed.
As the motor accelerates, the current will start to drop, but will not drop significantly until the motor reaches high speed, typically about 85% of synchronous speed. The actual starting current curve is a function of motor design and terminal voltage and is completely independent of motor load.
The motor load affects the time it takes for the motor to accelerate to maximum speed and therefore the duration of the high starting current, but not the magnitude of the starting current.
Provided that the torque developed by the motor exceeds the load torque at all speeds during the starting cycle, the motor will reach its maximum speed. If the torque supplied by the motor is less than the torque of the load at any speed during the start cycle, the motor will stop accelerating. If the starting torque with a DOL starter is insufficient for the load, the motor must be replaced with one that can develop a higher starting torque.
Acceleration torque is the torque developed by the motor minus the load torque, and will change as the motor accelerates due to the motor speed torque curve and the load speed torque curve. The starting time depends on the acceleration torque and the inertia of the load.
DOL starts have maximum starting current and maximum starting torque.
This could cause an electrical problem with the power supply, or it could cause a mechanical problem with the driven load. So it will be inconvenient for power line users. Always experience a voltage drop when starting a motor. But if this motor is not powerful, it will not affect much.
Different starting methods are used for starting induction motors because the induction motor draws more starting current when starting. In order to avoid damage to windings due to high starting current flow, we use different types of starters.
The simplest form of motor starter for the induction motor is the Direct On Line Starter. The direct-on-line (DOL) starter includes a circuit breaker, contactor and overload relay for protection. Electromagnetic contactor which can be opened by the thermal relay in the event of a fault.
Typically the contactor will be controlled by separate start and stop buttons and an auxiliary contact on the contactor is used, opposite the start button, as a hold contact. That is to say. the contactor is electrically interlocked and closed during engine operation.
Principle of the direct on-line starter (DOL)
To begin with, the contactor is closed, applying line voltage to the motor windings. The motor will draw a very high inrush current for a very short time, the magnetic field in the iron, and then the current will be limited to the locked rotor current of the motor. The motor will develop locked rotor torque and begin to accelerate to maximum speed.
As the motor accelerates, the current will start to drop, but will not drop significantly until the motor reaches high speed, typically about 85% of synchronous speed. The actual starting current curve is a function of motor design and terminal voltage and is completely independent of motor load.
The motor load affects the time it takes for the motor to accelerate to maximum speed and therefore the duration of the high starting current, but not the magnitude of the starting current.
Provided that the torque developed by the motor exceeds the load torque at all speeds during the starting cycle, the motor will reach its maximum speed. If the torque supplied by the motor is less than the torque of the load at any speed during the start cycle, the motor will stop accelerating. If the starting torque with a DOL starter is insufficient for the load, the motor must be replaced with one that can develop a higher starting torque.
Acceleration torque is the torque developed by the motor minus the load torque, and will change as the motor accelerates due to the motor speed torque curve and the load speed torque curve. The starting time depends on the acceleration torque and the inertia of the load.
DOL starts have maximum starting current and maximum starting torque.
This could cause an electrical problem with the power supply, or it could cause a mechanical problem with the driven load. So it will be inconvenient for power line users. Always experience a voltage drop when starting a motor. But if this motor is not powerful, it will not affect much.







No comments